WOC 560
Page 560
Mathematics
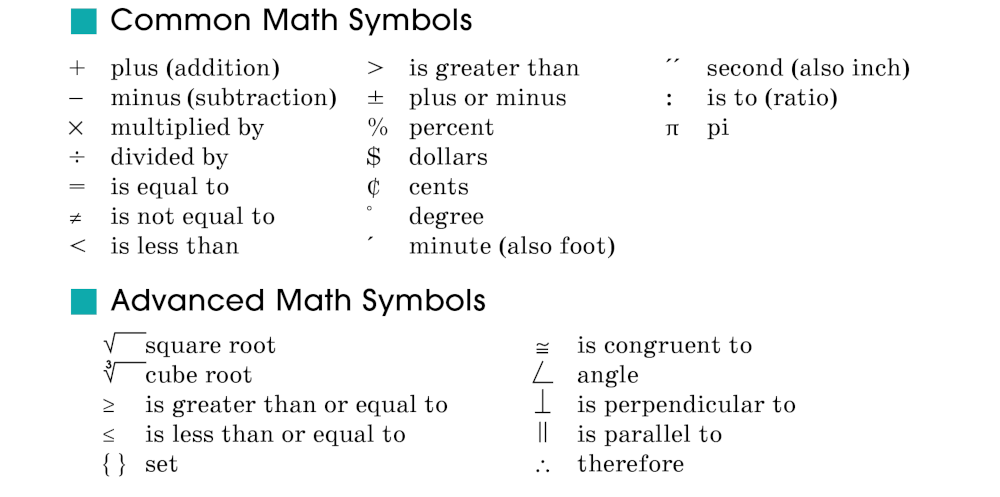
This section is your guide to the language of mathematics. It lists and defines many of the common (and not so common) mathematical signs, symbols, shapes, and terms. The section also includes helpful math tables.

WOC 561
Page 561


WOC 562
Page 562
Math Terms
Addition (+) is combining numbers to get a total, which is called a sum. The sum of 3 plus 5 is 8; 3 + 5 = 8.
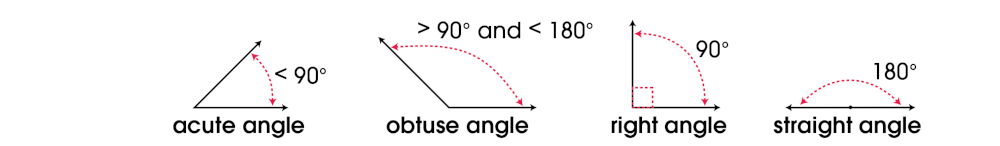
An angle is made when two rays (lines) share a common endpoint. An angle is measured in degrees.
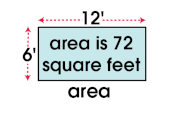
Area is the total surface within a closed figure (circle, square, etc.). The area of a rectangle is figured by multiplying the length by the width. Area is measured in square units such as square inches or square feet.
The average is found by adding a group of numbers together and then dividing that sum by the number of separate numbers (addends). The average of 7, 8, and 9 is 8, because 7 + 8 + 9 = 24, and 24 ÷ 3 (numbers) = 8. This is also called the mathematical mean.

A circle is a round, closed figure. All the points on its circumference (edge) are the same distance from the center of the figure.
Circumference is the measure of distance around the edge of a circle.
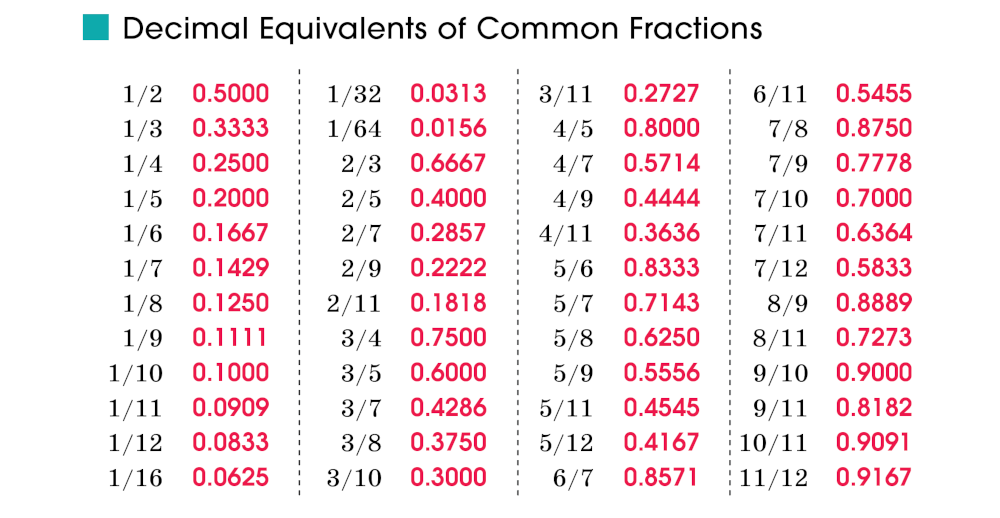
A common denominator is a multiple shared by the denominators of two or more fractions. For example, 6 is a common denominator of 1/2 and 1/3 because 6 is a multiple of both 2 and 3. To add or subtract fractions, you must find a common denominator; 1/2 + 1/3 = 3/6 + 2/6 = 5/6. The lowest common denominator is also called the least common multiple (LCM) of the denominators.

Congruent (≅) is the term for two figures, angles, or line segments that are the same size and shape.
Data are numbers collected to compare.
A decimal is a fraction written in the decimal number system. (Decimal means “based on the number 10.”) Decimals are written using a decimal point and place values—tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on. The fraction 1/2 is 0.5, or 5/10.
WOC 563
Page 563

A degree is a unit of measurement for angles and arcs. It is written as a small circle [°]. You can write 90° or 90 degrees. There are 360 degrees in a circle.
The denominator is the bottom number of a fraction. In the fraction 1/3, the denominator is 3. It indicates the number of parts needed to make a whole unit.
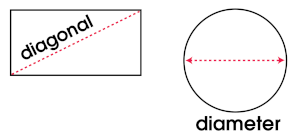
A diagonal is a line from one vertex (corner) of a quadrilateral to the opposite vertex.
The diameter is the length of a straight line through the center of a circle.
A dividend is a number to be divided. In the equation 12 ÷ 2 = 6, 12 is the dividend.
Division (÷) is a basic math operation used to determine how many times one quantity is contained in another. Division tells you how many times you have to subtract a number to reach zero. For example, 10 ÷ 5 = 2 because you subtract 5 two times to reach zero (10 – 5 = 5; 5 – 5 = 0).
The divisor is the number that divides the dividend. In the statement 12 ÷ 2 = 6, 2 is the divisor.
An equation is a statement that says two numbers or mathematical expressions are equal to each other (2 + 10 = 12 or x + 4 = 9). Equations use the equal sign (=).
An estimate is a reasonable guess at an answer. If you add 6.24 and 5.19, you can estimate the answer will be around 11, because 6 + 5 = 11.
An even number is a number that can be divided by 2 without having a remainder (2, 4, 6, and so on). For example, 4 ÷ 2 = 2.
An exponent is the small, raised number to the right of the base number that shows how many times the base is to be multiplied by itself. In the expression 23, 3 is the exponent (2 is the base). So 23 means you need to multiply 2 three times (2 × 2 × 2 = 8).
A factor is a number that is being multiplied. In 4 × 3 = 12, the factors are 4 and 3.
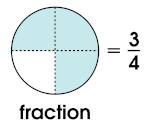
A fraction is a number that expresses a part of a whole. In the fraction 3/4, 4 is the denominator—the number of equal parts that make up the whole. The number 3 is the numerator—the number of parts being talked about.
WOC 564
Page 564
Geometry is the study of two-dimensional shapes (circles, triangles), three-dimensional solids (spheres, cubes), and positions in space (points).
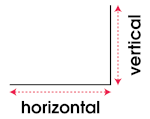
A horizontal is a line parallel to the earth’s surface, or horizon, going across rather than up and down. A vertical is a line that is straight up and down and perpendicular to the horizon.
A hypotenuse of a right triangle is the side opposite the right angle.
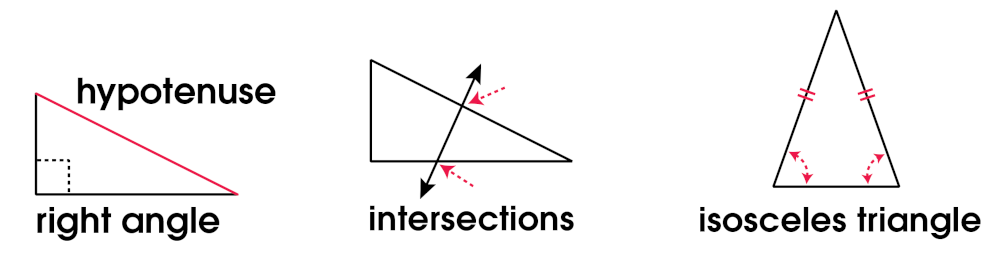
An intersection is the point where two lines in geometry cross each other.
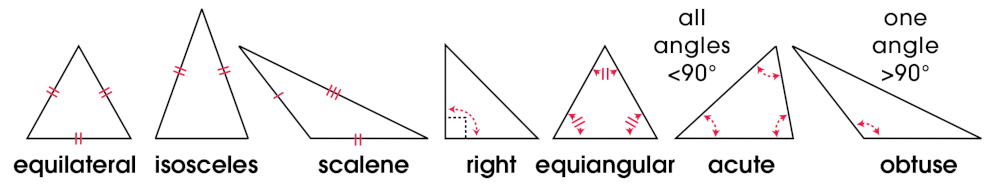
An isosceles triangle is a triangle with two sides of equal length and two equal angles. (See triangle.)
Length is the distance along a line from one point to another.

A line is all points formed by extending a line segment both directions, without end.
Lowest common denominator (See common denominator.)
Mean is another word for average. (See average.)
The median is the middle number when a group of numbers is arranged in order from the least to the greatest, or the greatest to the least. In 1, 4, 6 the median (middle number) is 4. In 1, 4, 6, 8 the median is 5, the average of the two middle numbers: 4 + 6 = 10; 10 ÷ 2 = 5.
A multiple is a quantity into which another quantity can be divided, with zero as the remainder (both 6 and 9 are multiples of 3).
Multiplication (×) is like addition because you add the same number a certain number of times (2 × 4 = 4 + 4). When you multiply numbers, the answer is called the product. The product of 2 times 4 is 8 because 2 ✕ 4 = 8. (A raised dot also means multiplication. 2 × 3 is the same as 2 • 3.)
The numerator is the top number of a fraction. In the fraction 6, the numerator is 5.
An obtuse angle is an angle greater than 90 degrees and less than 180 degrees. (See angle.)
An odd number is a number that cannot be divided evenly by 2. The numbers 1, 3, 5, 7, and so on, are odd numbers.
WOC 565
Page 565

Opposite numbers are any two numbers whose sum is zero (–2 and +2 are opposite numbers).
Parallel refers to lines that never intersect.
Percent is a way of expressing a number as a fraction of 100. (Percent means “per hundred.”) The percent symbol is %. So 1/2 expressed as a percentage is 50/100, which is 50%.
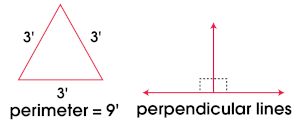
The perimeter is the distance around the edge of a multi-sided figure. If a triangle has three sides, each 3 feet long, its perimeter is 9 feet (3 + 3 + 3 = 9).
Perpendicular refers to two lines that intersect, forming right angles (90° angles).
Pi (π) is the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter. Pi is approximately 3.14.
Place value is the value of the place of a digit depending on where it is in the number.
3,497 is 3 thousands, 4 hundreds, 9 tens, 7 ones
0.3497 is 3 tenths, 4 hundredths, 9 thousandths, 7 ten-thousandths
A point is an exact location on a line or plane or in a space.
A positive number is a number greater than 0.
A prime number is a number that cannot be divided evenly (without a remainder) by any number except itself and 1. The number 6 is not a prime number because it can be divided evenly by 1, 2, 3, and 6. The number 5 is a prime number because it can be divided evenly only by itself (5) and 1.
Product is the word used to indicate the result of multiplication. For example, 8 is the product of 2 times 4, because 2 × 4 = 8.
The quotient is the number you get when you divide one number by another number. If 8 is divided by 4, the quotient is 2, because 8 ÷ 4 = 2.
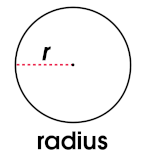
The radius (r) is the distance from the center of a circle to its circumference. (The radius is half the diameter.)
A ratio is a way of comparing two numbers by dividing one by the other. The ratio of 3 to 4 is 3/4. If there are 20 boys and 5 girls in your class, the ratio of boys to girls is 20/5 (4/1 in lowest terms), or 4:1.
WOC 566
Page 566
A rectangle is a four-sided closed figure with four right angles and with opposite sides parallel and congruent.
A right angle is an angle that measures 90 degrees. A right angle is formed when two perpendicular lines meet. (See angle.)
Rounding gives you an approximate number if you don’t need an exact one. If 2,323 people attended a soccer game, about 2,000 people were there. If 2,857 people attended, about 3,000 were there. Round up if the number is halfway or more to the next highest number (2,500 is halfway between 2,000 and 3,000). Round down if the number is less than halfway.
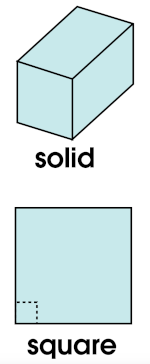
A solid is a three-dimensional figure in geometry, like a cube, a cone, a prism, or a sphere.
A square is a rectangle that has four sides of equal length and four right angles. Square also refers to the product of a number multiplied by itself. The square of 4 is 16 (42 = 16; 4 × 4 = 16). (See area for another use of “square.”)
The square root of a number is a number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number as the product. The symbol for square root is √. The square root of 4 is 2, because 2 × 2 = 4 ( √4 = 2).
Subtraction (–) is the inverse (opposite) of addition. Instead of adding one number to another, you take one number away from another. When you subtract two numbers, you find the difference between them. So 11 – 6 = 5.
The sum is the number you get when you add numbers. For example, 7 is the sum of 4 and 3, because 4 + 3 = 7.
A triangle is a closed figure with three sides. The sum of the angles in every triangle is 180°. Triangles can be classified by sides: equilateral, isosceles, or scalene; or by angles: right, equiangular, acute, or obtuse.

A vertex is the point where two sides of a plane (flat) figure meet (corner). The plural of vertex is vertices.
Vertical (See horizontal.)