WOC 122
WOC 123
Page 123

Choosing the Best Form
At a restaurant, you have a lot of menu options. What will you have? That depends. What time of day is it? How hungry am I? What foods do I like best? What foods am I allergic to? You think of all these things as you settle on the perfect meal.
When you are choosing a writing form, you go through a similar process. You ask yourself these questions:
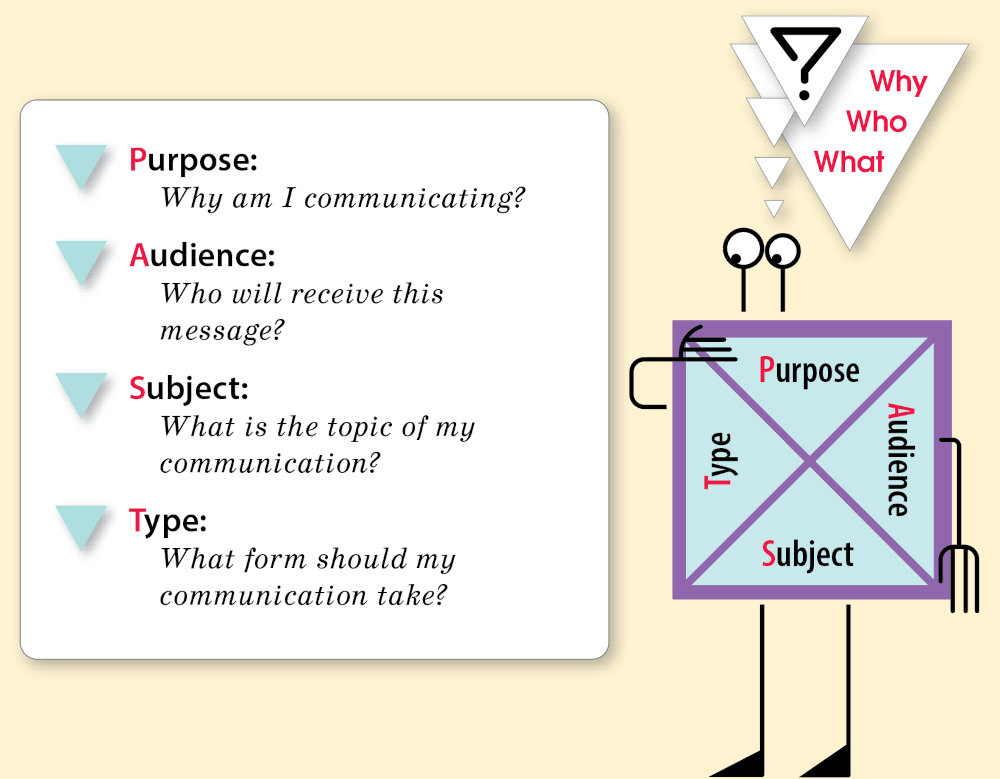
- Why am I writing?
- Who are my readers?
- What am I writing about?
Answering these questions will help you choose the best form for any communication situation. Then you can dig in!
What’s Ahead
WOC 124
Page 124
Quick Guide ■ Choosing Forms
Every time you communicate, you have a specific purpose for connecting with your audience about a particular subject. When you understand all of the parts of a communication situation, you can choose the best type of communication to use. The PAST strategy can help. (Learn more.)
Link to the Traits
Each form of communication relies on these three traits:
Ideas ■
The big ideas are your subject and topic. The specific message you want to deliver is your focus as well as the details you share about it.
Organization ■
You organize ideas to help readers understand them: chronologically, spatially, comparing and contrasting, showing cause and effect, and so on.
Voice ■
Your voice represents you and connects with your reader. It also should be appropriate to your topic and purpose as well as the form you are using.
WOC 125
Page 125
A Closer Look
Whenever you communicate, think about your purpose, audience, and subject. They will help you decide on the type or form of your communication. These sample analyses show how.



WOC 126
Page 126
Communication Options
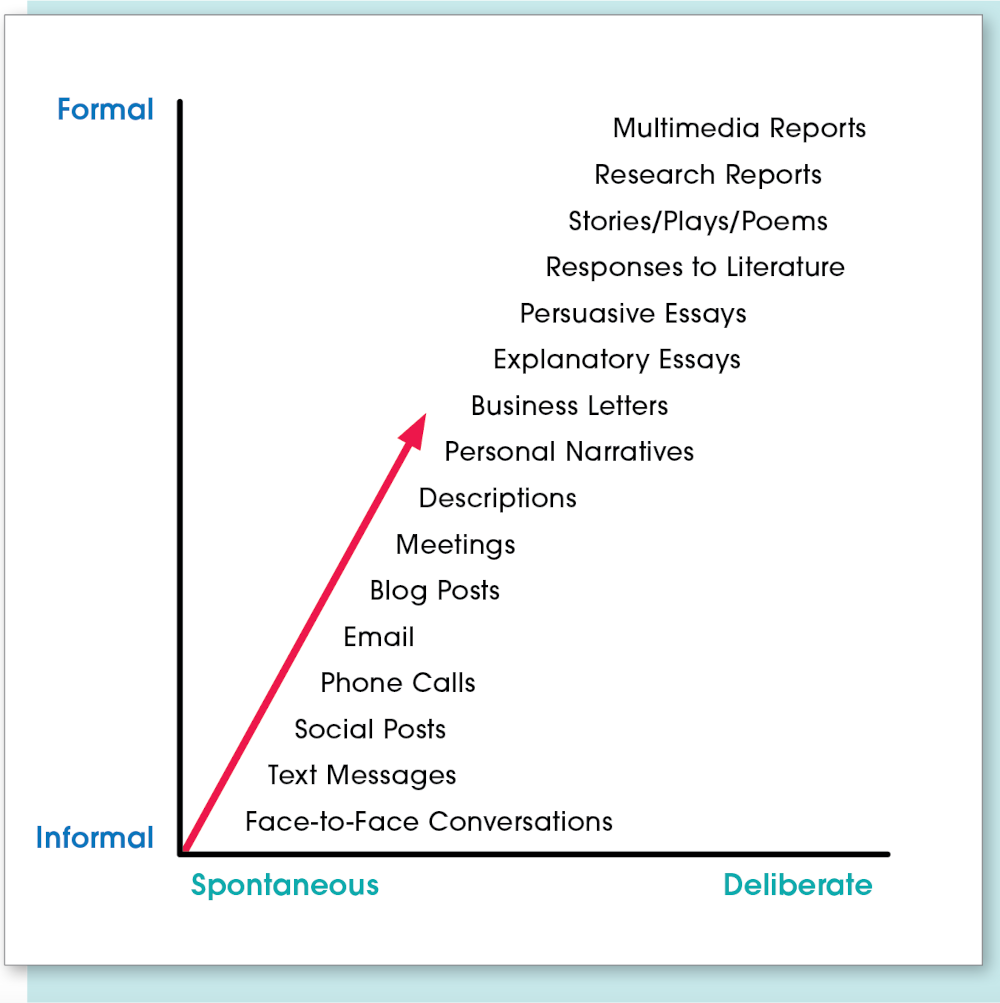
Not all forms of communication are created equal. Some forms are spontaneous and informal. Others are more deliberate and formal. The following chart gives an overview of these differences.
The Continuum of Communication

Helpful Hint
When deciding on a form of communication, consider the importance of your message and the time you have to communicate it. Do you want a lasting record of the communication? Finally, think about your audience and how they may respond to whatever form you choose.
WOC 127
Page 127
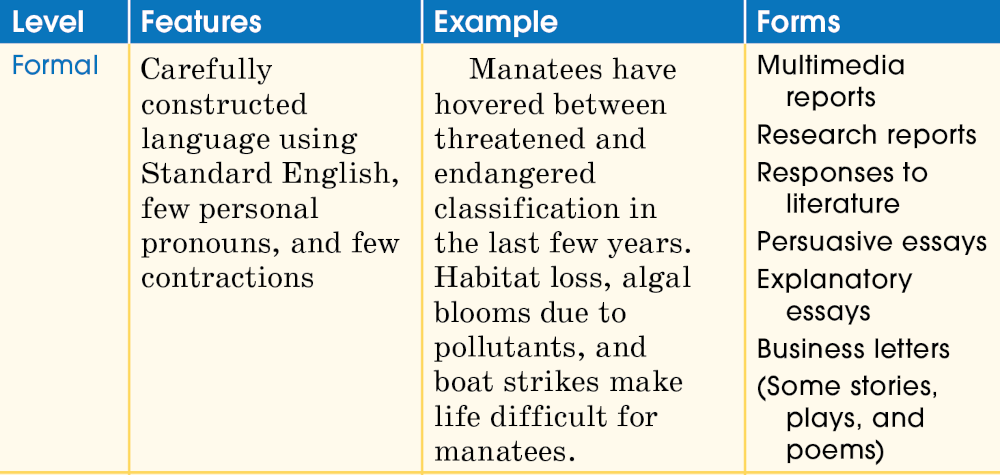
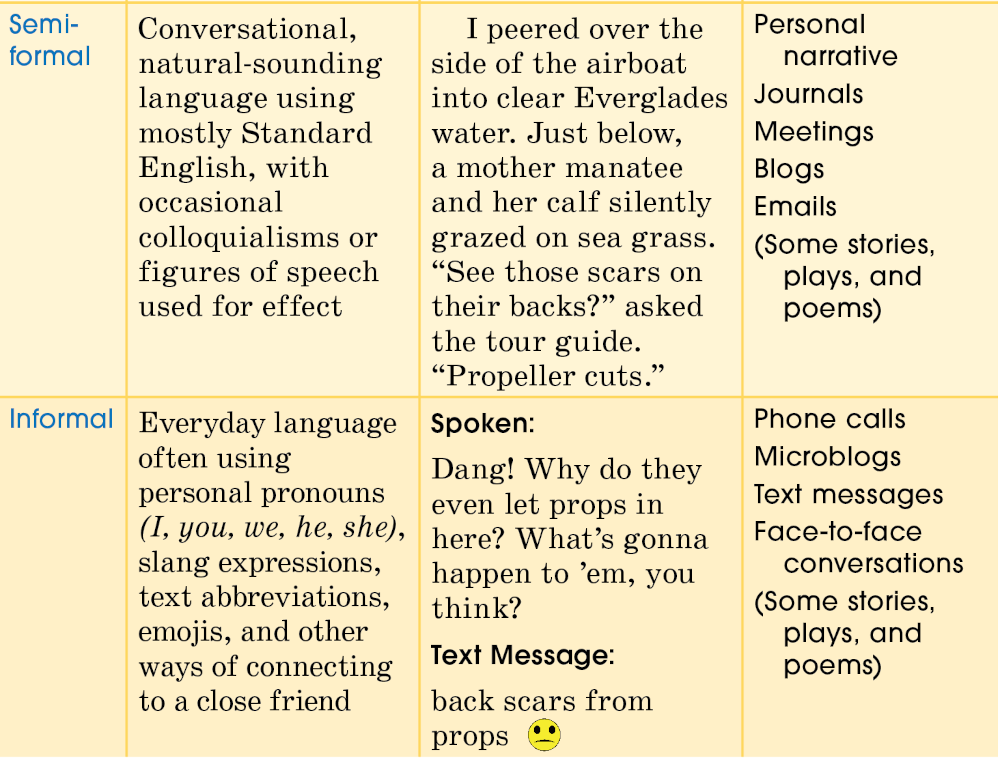
Levels of Language
Language is like clothing: It can be extremely casual, extremely formal—or somewhere in between. You wouldn’t wear a swimsuit to a formal dance or a tuxedo to the beach. In the same way, you wouldn’t use emojis in an essay or transitions such as “furthermore” in a text message. The chart below shows the different levels of language.
© 2026 Thoughtful Learning. Copying is permitted.
k12.thoughtfullearning.com