WT 354
Page 354
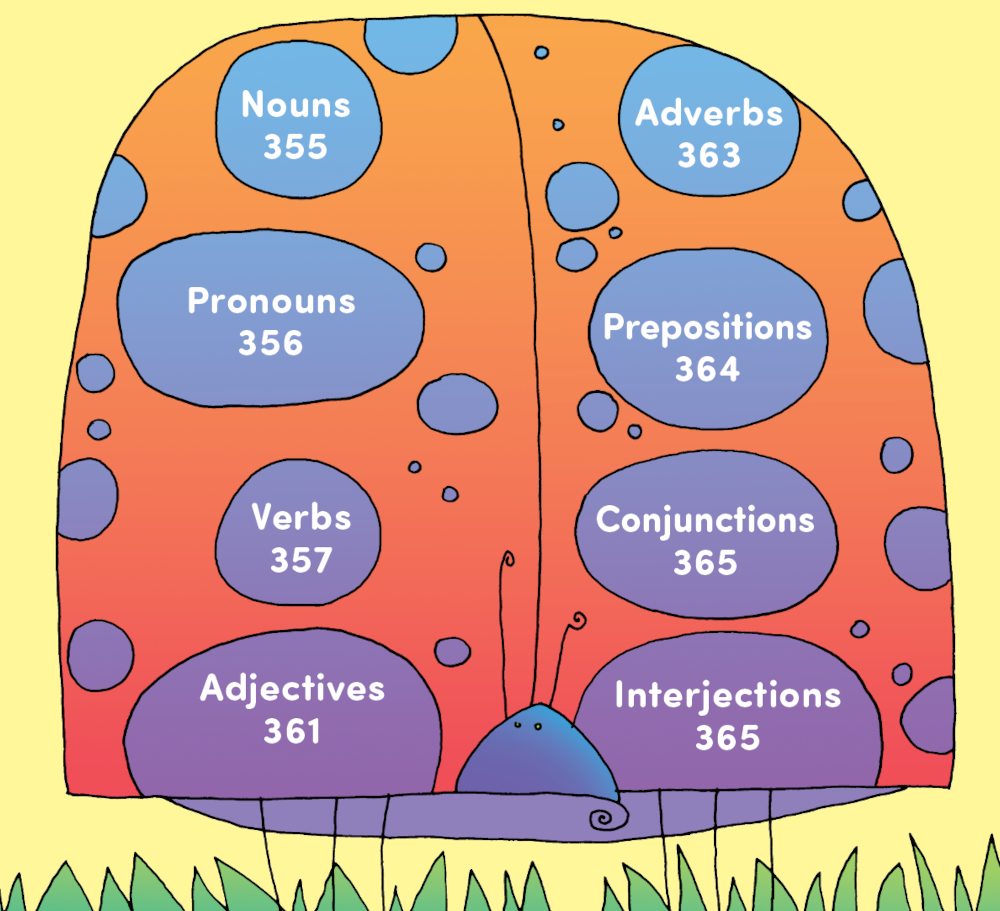
Understanding Our Language
The words in our language fit into eight groups called the parts of speech.
WT 355
Page 355
Nouns
A noun names a person, a place, a thing, or an idea.
coach Chicago beagle love
Kinds of Nouns
Common Nouns
A common noun names any person, place, thing, or idea.
teacher school class math
Proper Nouns
A proper noun names a specific person, place, thing, or idea. Proper nouns are capitalized.
Eli the Pentagon the Bucks Islam
Singular Nouns
A singular noun names one person, place, thing, or idea.
cousin park pencil moral
Plural Nouns
A plural noun names more than one person, place, thing, or idea.
cousins parks pencils morals
Possessive Nouns
A possessive noun shows ownership.
My dog’s collar is shiny red.
(Add ’s to form most singular possessives.)
My cats’ collars are green and blue.
(Add only ’ to form most plural possessives.)
 © Thoughtful Learning 2025
© Thoughtful Learning 2025
Singular Nouns
A singular noun names one person, place, thing, or idea.
cousin park pencil moral
Plural Nouns
A plural noun names more than one person, place, thing, or idea.
cousins parks pencils morals
Possessive Nouns
A possessive noun shows ownership.
My dog’s collar is shiny red.
(Add ’s to form most singular possessives.)
My cats’ collars are green and blue.
(Add only ’ to form most plural possessives.)

WT 356
Page 356
Pronouns
A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun.
Beth said she would come to my birthday party.
(The pronoun she replaces the noun Beth.)
My cake is ready, and Mom will pick it up.
(The pronoun it replaces the noun cake.)
Kinds of Pronouns
Possessive Pronouns
A possessive pronoun shows ownership.
Gato left his fur on the love seat.
(Gato’s fur)
Our love seat needs to be vacuumed.
(The family’s love seat)
Common Personal Pronouns
| Singular Pronouns | Plural Pronouns |
I, me, my, mine, |
we, us, our, ours, |
you, your, yours, |
you, your, yours, |
he, him, his, she, her, hers, it, its |
they, them, their, theirs |
WT 357
Page 357
Verbs
A verb shows action or links two ideas in a sentence.
I jump my bike off the ramp for three feet of air.
I am thrilled and a little terrified.
Types of Verbs
Action Verbs
An action verb tells what the subject is doing.
A robin hunts worms in our yard.
The worms flee underground like people running from Godzilla.
Linking Verbs
A linking verb links the subject to a word in the predicate part of a sentence. (The predicate tells what the subject is or does.)
The robin is a giant monster.
(The verb is links robin to monster.)
The worms are afraid.
(The verb are links worms to afraid.)
Linking Verbs:
is, am, are, was, were, be, been
Helping Verbs
A helping verb comes before the main verb, and it helps state an action or show time.
I will scare the robin away.
(Will helps the main action verb scare.)
The worms will call me “Mothra.”
(Will helps the main linking verb call.)
Helping Verbs:
has, have, had, will, could, should, would, do, did, may, can
WT 358
Page 358
Tenses of Verbs
The tense of a verb tells when an action takes place. Tense is often shown by endings (lives, lived) and by helping verbs (will live, has lived).
Present Tense Verbs
Present tense means the action is happening now or that it happens all of the time.
Latrice loves soccer.
Her friends want to form a team.
Past Tense Verbs
Past tense means the action happened before, or in the past.
Yesterday they played in the park.
The girls learned new footwork.
Future Tense Verbs
Future tense means the action will take place at a later time, or in the future.
Tomorrow Latrice will play goalie.
The girls will challenge another team.
Some verbs tell the time of the action in other ways.
Latrice has played for three years.
The team is planning a tournament.
The soccer field had been a baseball diamond.
WT 359
Page 359
Forms of Verbs
Singular Verbs
The verb in a sentence must agree, or make sense, with the subject. Use a singular verb when the subject is singular. Remember that singular means “one.”
Derrick folds paper airplanes.
(Folds is a singular verb.)
He holds flying competitions.
(Holds is a singular verb.)
Plural Verbs
Use a plural verb when the subject is plural. Remember that plural means “more than one.”
His planes fill a shelf in his room.
(Fill is a plural verb.)
They vary from gliders to stunt planes.
(Vary is a plural verb.)
Regular Verbs
Regular verbs add ed to form the past tense.
He invents. Yesterday he invented.
We watch. We have watched.
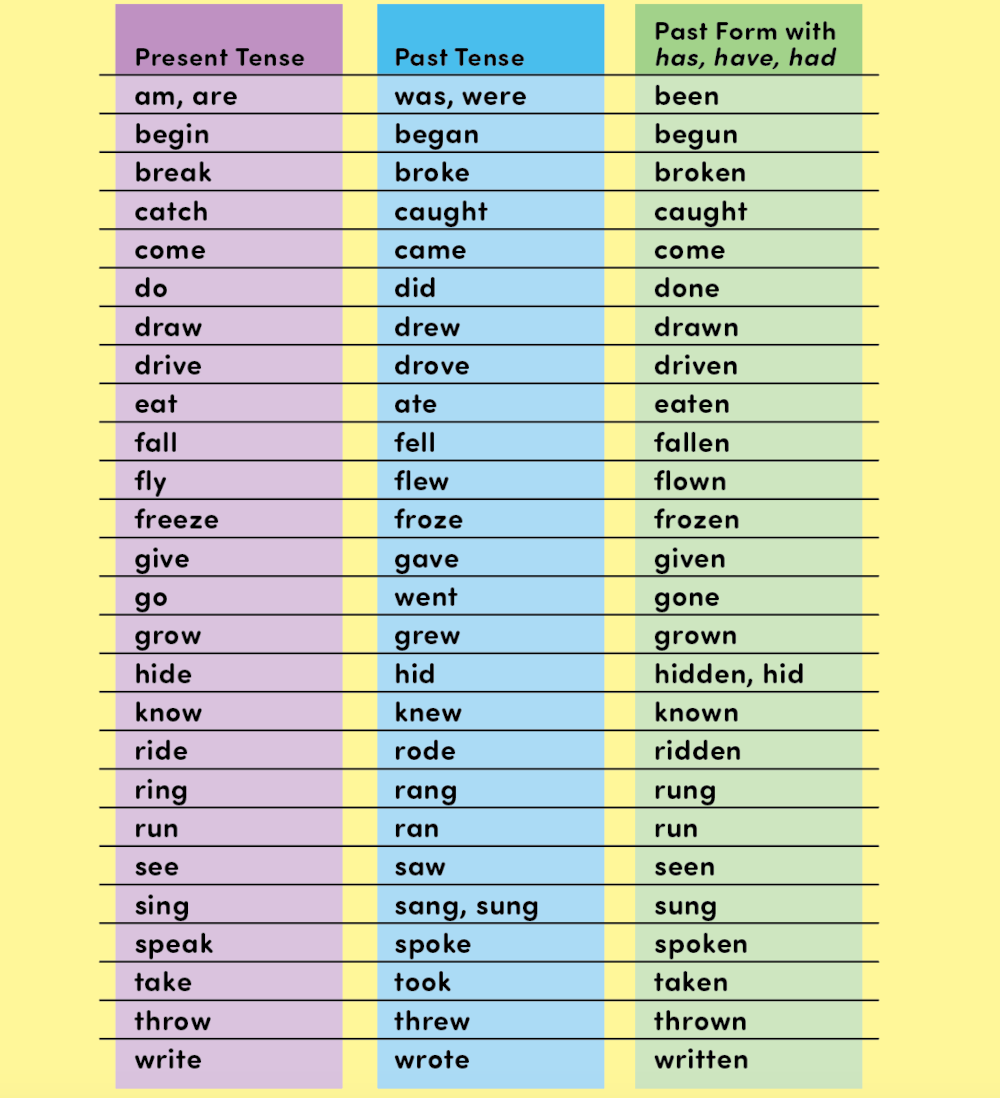
Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs change to form the past tense. (See the next page for a chart.)
I see. I saw. I have seen.
We fly. We flew. We have flown.
The most common irregular verb is be. Different forms of the verb include am, is, are, was, were, and been.
WT 360
Page 360
Common Irregular Verbs
WT 361
Page 361
Adjectives
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or a pronoun. Adjectives tell what kind, how many, or which one.
Most alligators live in coastal marshes.
(An adjective usually comes before the word it describes.)
Alligators in Louisiana bayous are legendary.
(An adjective may come after a linking verb like is or are.)
Articles
The articles a, an, and the are adjectives.
An alligator is an American reptile.
(An is used before words beginning with a vowel sound.)
A crocodile is a relative in Africa.
(A is used before words beginning with a consonant sound.)
Kinds of Adjectives
Proper Adjectives
Proper adjectives are formed from proper nouns. They are always capitalized.
I spotted an American alligator.
Compound Adjectives
Compound adjectives are made up of more than one word. Some are spelled as one word, and some are hyphenated.
It lived in a wetland habitat.
Alligators are meat-eating reptiles.
WT 362
Page 362
Forms of Adjectives
Positive Adjectives
Positive adjectives describe without making a comparison.
A mastiff is a massive dog.
Comparative Adjectives
Comparative adjectives compare two people, places, things, or ideas.
Maltese are smaller than pugs.
(Comparative adjectives often end in er.)
Rottweilers are more muscular than golden retrievers.
(The word more is used before some adjectives with two or more syllables.)
Superlative Adjectives
Superlative adjectives compare three or more people, places, things, or ideas.
That Great Dane is the tallest dog I have ever seen.
(Superlative adjectives often end in est.)
Collies are among the most intelligent dogs.
(The word most is used before some adjectives with two or more syllables.)
Irregular Forms of Adjectives
Irregular adjectives change to create comparative and superlative forms.
|
Positive |
Comparative |
Superlative |
|
good |
better |
best |
|
bad |
worse |
worst |
|
many |
more |
most |
WT 363
Page 363
Adverbs
Adverbs describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Adverbs tell when, where, or how an action is done.
Snakes slither expertly without needing legs.
They push repeatedly on the ground with their coils.
Adverbs often end with ly, but not always. Words like not, never, very, and always are common adverbs.
Kinds of Adverbs
Adverbs of Time (When)
Adverbs of time tell when or how often an action is done.
Snakes often shed their old skin.
A growing snake could molt monthly.
Adverbs of Place (Where)
Adverbs of place tell where something happens.
Snakes live almost everywhere.
Sidewinders move sideways.
Adverbs of Manner (How)
Adverbs of manner tell how something is done.
Rattlesnakes move cautiously.
Their tails rattle angrily.
WT 364
Page 364
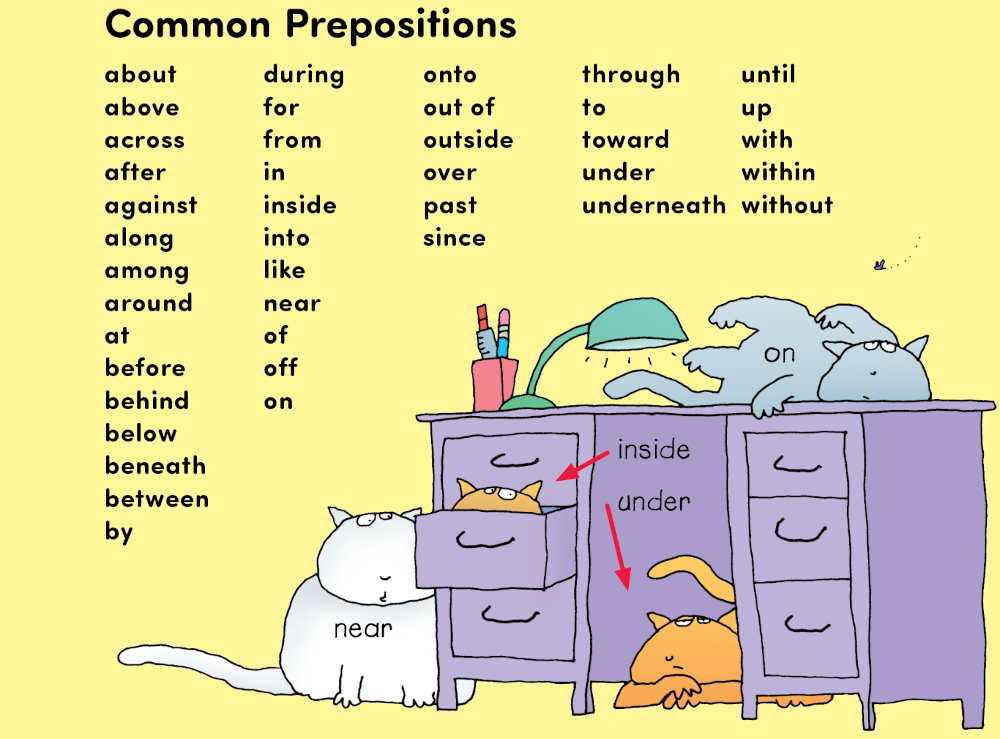
Prepositions
Prepositions tell position or direction. They often introduce prepositional phrases.
Tiger slept under the desk.
(Under tells position.)
Remington jumped onto the desk.
(Onto tells direction.)
Prepositional Phrases
A prepositional phrase begins with a preposition and ends with a noun or a pronoun.
Gato hides inside the drawer.
Sforzando lurks near the desk.
WT 365
Page 365
Conjunctions
Conjunctions connect words or groups of words.
Coordinating Conjunctions
Coordinating conjunctions connect equal words, phrases, or clauses:
and but or nor for so yet
We splashed and ran.
(And connects two equal words.)
We played with the hose and in the sprinkler.
(And connects two equal phrases.)
We wore sunscreen but we still got a little red.
(But connects two equal clauses.)
Other Conjunctions
Other conjunctions show that one idea is less important than another:
after before until where because since when while
I catch fireflies when it gets dark.
(When it gets dark is less important.)
I let each one go after I make a wish.
(After I make a wish is less important.)
Interjections
An interjection is a word or phrase used to express strong emotion or surprise. It is followed by an exclamation point or by a comma.
Yay! Woot! Wow, I made seven wishes!
Teacher Support:
Click to find out more about this resource.
© 2026 Thoughtful Learning. Copying is permitted.
k12.thoughtfullearning.com