Strong writing has three qualities: effective structure, strong ideas, and correct conventions. The new standards and assessments seek these three qualities in student writing.
Structure
Structure refers to the large-scale and small-scale organization of writing.
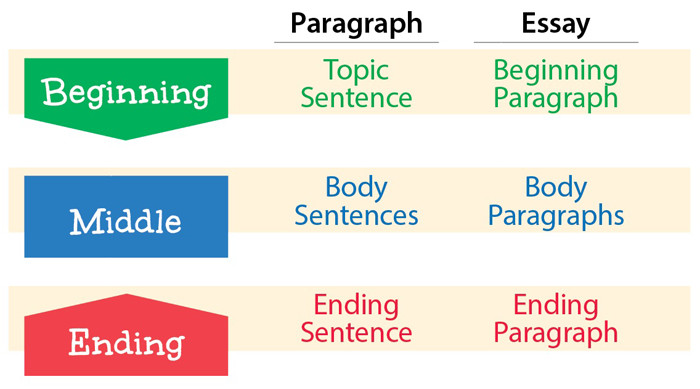
On the large scale, effective structure has three parts:
- A beginning that connects to the reader and introduces the topic.
- A middle part that explores and explains the topic for the reader.
- An ending that sums up the writing and provides a strong final thought.
Three-Part Structure
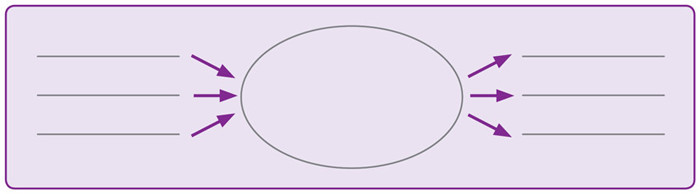
On the small scale, effective structure organizes ideas to achieve a purpose. For example, narratives often use a time-order pattern, persuasive (argument) writing may use a problem-solution pattern, and explanatory writing may use a cause-effect pattern.
Time-Order

Problem-Solution

Cause-Effect
Ideas
Ideas refer to what the writer is trying to convey to the reader. The ideas include the big thinking that the writer is doing as well as all the little details.
On the large scale, ideas include the big thoughts:
- The subject is the broad area of thought that writing addresses. Sometimes, students start an assignment with a broad subject area like those in the Basics of Life list below:
Basics of Life
Animals
Art
Books
Career
Communication
Community
Culture
Education
Energy
Entertainment
Environment
Exercise
Family
Fantasy
Fashion
Food
Freedom
Friends
Fun
Future
Geography
Goals
Government
Health
History
Holidays
Home
Imagination
Language
Law
Life
Literature
Love
Medicine
Money
Music
Nature
Occupation
People
Personality
Plants
Play
Recreation
Rights
Rules
Science
Seasons
Self
Sports
Technology
Transportation
Travel
Vehicles
Work
- The topic is the specific part of the general subject. For example, if a student picks the general subject of “Family,” the specific topic could be “My eighth birthday party with my family.”
- The focus (thesis) is the exact thought or feeling the author gives about the topic. The focus for the story about the eighth birthday party could be that the best gift was having his father return from the war.
On the small scale, the writer uses many supporting details to develop the big ideas. These details need to be precise and correct, of course. Different types of ideas provide different types of support. For example, facts and statistics connect ideas to reality, whereas anecdotes and sensory details connect ideas to emotion.
Conventions
The third quality of writing refers to the correct use of the rules of English:
- Punctuation involves using periods, commas, quotation marks, and other writing signposts to help the reader understand the ideas.
- Capitalization is the correct use of upper- and lowercase letters.
- Spelling is, of course, correct spelling.
- Usage refers to using the right word in each situation.
- Grammar refers to the correct use of the parts of speech: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, and so on.